How to Document Foraging Locations?
Keeping a record of your foraging spots is crucial for anyone passionate about wild food. It helps you track your finds and enriches your foraging experiences.
This article delves into various methods for documenting your foraging spots, contrasting traditional techniques with modern technological advancements. You will find guidance on selecting the best approach tailored to your needs, along with tips for creating an effective foraging log.
We will explore the benefits and drawbacks of sharing your discoveries.
Whether you re just starting out or have years of experience under your belt, this guide is designed to provide you with insights that will enrich your foraging adventures.
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- Ways to Document Your Foraging Spots
- Choosing the Best Method for You
- Creating a Foraging Location Log
- Tips for Maintaining and Updating Your Log
- Sharing Your Foraging Locations
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is considered a foraging location?
- Why is it important to document foraging locations?
- How do I document a foraging location?
- What should I include in my documentation of a foraging location?
- Can I document foraging locations for personal use?
- How can I contribute my records of foraging locations to scientific research?
Key Takeaways:
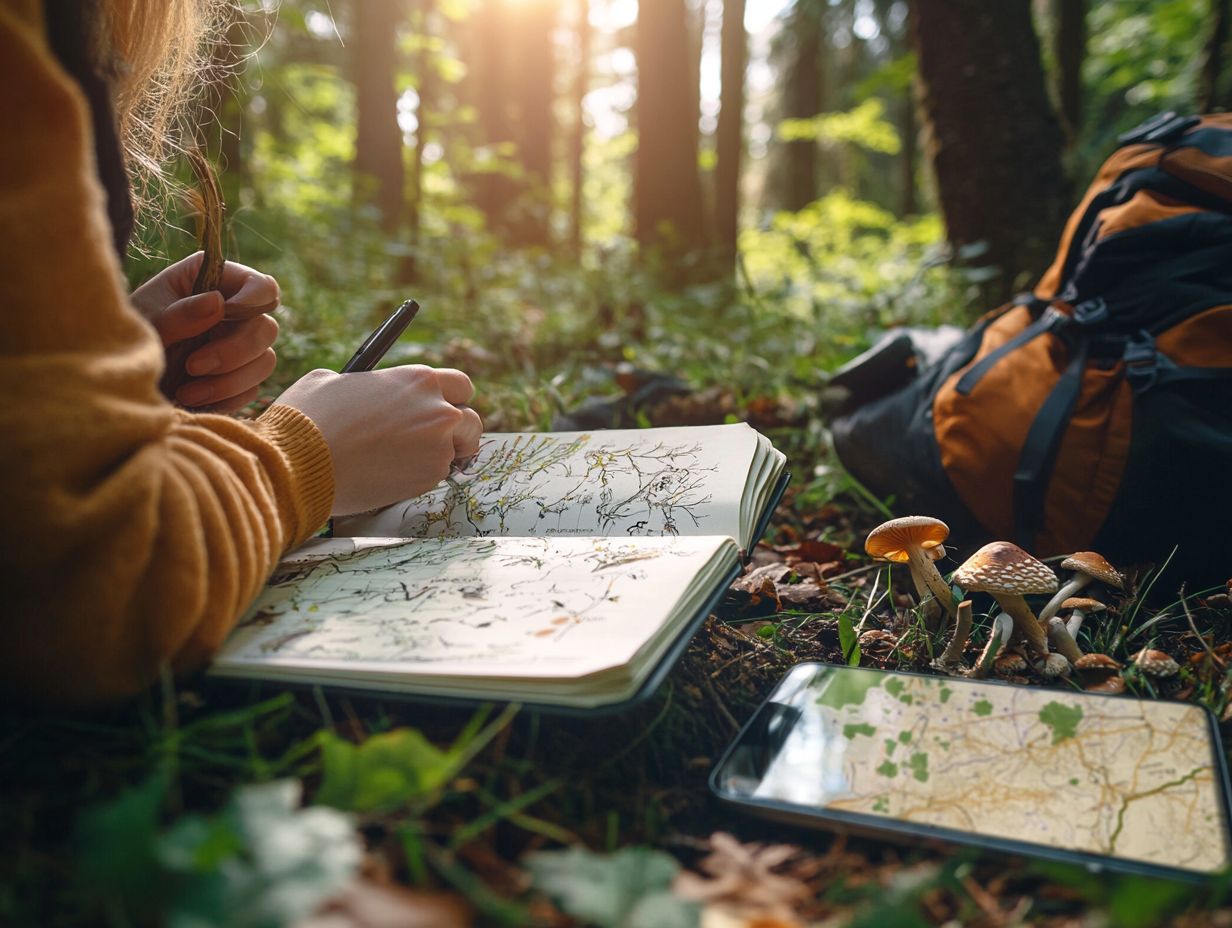

- Keep a record of your foraging locations to improve your future foraging experiences.
- Consider factors such as accessibility and personal preference when choosing a method.
- Include details like plant names and harvest dates to track your success.
Why Document Foraging Locations?
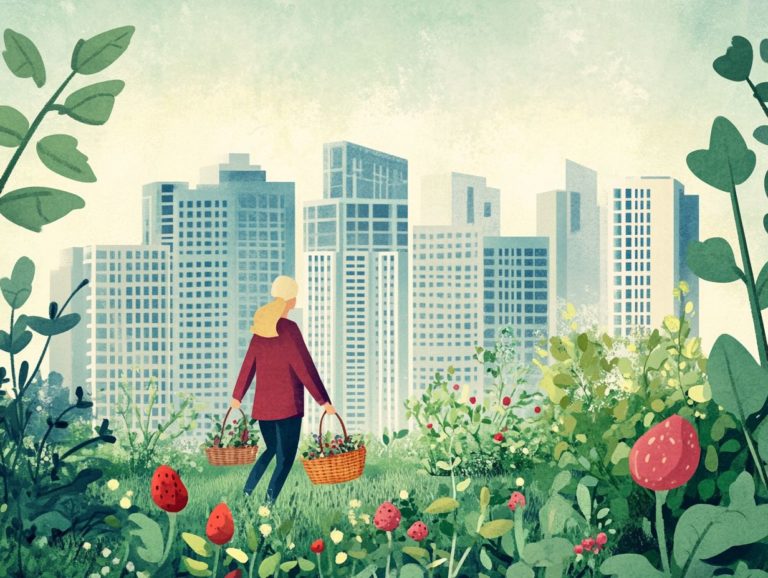
Documenting your foraging locations is essential if you’re passionate about urban foraging. It showcases the seasonal bounty of falling fruit and edible plants while building a sense of community among fellow foragers. By sharing information about food sources in public parks and urban gardens, you contribute to environmental awareness and sustainability. This practice provides insights into local biodiversity, helps minimize food waste, and promotes the idea of food liberation, which means having access to free, wild food in your community.
When you keep detailed records of your foraging spots, you enhance community engagement. This opens the door to collaborative workshops and knowledge exchanges that enable novice foragers to thrive. Your documented sites become educational resources, championing food ethics and highlighting the importance of respecting nature and practicing sustainable harvesting methods.
Preserving the locations of edible species is vital for local ecology. It helps protect and elevate native plants while encouraging responsible stewardship of urban green spaces. Ultimately, these initiatives foster a culture of appreciation for the natural bounty around you, creating a richer, more connected community.
Ways to Document Your Foraging Spots
You have various methods at your disposal for documenting foraging locations. Traditional techniques like handwritten notes and tree inventories stand alongside modern technology that leverages platforms like Google Maps. To enhance your skills, consider learning how to document your foraging experiences.
With these tools, you can craft interactive maps that vividly illustrate the food resources in your area. By blending these approaches, community foragers can seamlessly share and access invaluable information about edible plants and fruit trees scattered throughout urban landscapes.
Traditional Methods vs. Modern Technology
Traditional methods of documenting foraging locations often involve handwritten logs, maps, and community discussions. However, modern technology can elevate your foraging game. Apps and online platforms make documentation faster and more efficient, especially when learning how to plan a foraging trip, opening the door to urban foraging for a wider audience. These tools enhance collaboration among fellow foragers and encourage sharing knowledge about edible species across locations.
While there’s undeniable charm in a handwritten log, with its personal touch and historical significance, it simply can’t compete with the immediacy offered by technology. Imagine using apps that customize maps to spotlight areas rich in foraged goods. You can easily locate resources!
Local foraging groups now tap into platforms that utilize crowdsourced entries, which means contributions from many people, giving real-time updates on seasonal shifts and newly discovered edible plants. This harmonious blend of traditional wisdom and cutting-edge technology boosts the efficiency of urban foraging while cultivating a community spirit grounded in food ethics and environmental consciousness.
Choosing the Best Method for You

Selecting the ideal method for documenting your foraging locations depends on your preferences, accessibility, and the unique needs of your foraging endeavors or community group. For guidance, you can explore how to map your foraging routes, as different approaches cater to varying levels of expertise and engagement with food education.
Whether you re a novice or a seasoned forager, familiarizing yourself with the diverse options available can significantly enrich your foraging experience and promote sustainable practices.
Factors to Consider
When choosing a method to document your foraging locations, several key factors come into play:
- Your access to technology
- The level of community engagement you seek
- Your personal preferences regarding documentation methods
Understanding these elements is essential for you as a community forager. It allows you to effectively share and utilize information about edible plants and seasonal produce.
Your comfort with technology is paramount. You’ll want to feel at ease using apps, GPS, or online platforms to map your exciting discoveries. Local resources like foraging workshops or community gardens can also impact your chosen methods.
Input from your community is invaluable. Sharing insights and experiences deepens your understanding of sustainable practices while enriching collective knowledge. This openness fosters environmental stewardship and strengthens bonds among foragers, cultivating a culture of collaboration and respect for nature s abundance.
Creating a Foraging Location Log

Creating a foraging location log means systematically documenting vital information about edible plants and food resources. This includes noting their locations, seasonal availability, and how to document your foraging finds with detailed descriptions.
This practice not only benefits your own foraging endeavors but also enriches a broader knowledge base that supports sustainability and ecological conservation efforts within your community of foragers.
Your log can take many forms, ranging from a straightforward notebook to advanced digital applications. This allows you to tailor it to your specific needs and preferences.
What Information to Include
A comprehensive foraging location log should capture crucial details like:
- Species identification
- Descriptions of edible plants
- Their precise locations
- The seasonal produce available
This information enables you as a community forager to effectively locate food sources while championing environmental sustainability.
With this knowledge, you can make informed decisions when foraging and encourage responsible practices among fellow enthusiasts.
A well-maintained log serves as an invaluable educational tool, guiding urban gardeners and food lovers alike in appreciating the biodiversity surrounding them. By documenting specific characteristics of each plant such as habitat preferences and growth patterns you deepen your understanding and appreciation for local ecosystems.
Seasonal availability is particularly important. It helps you recognize the optimal times to harvest specific species, contributing to sustainable practices within your community. Engaging with a community foraging log enriches your personal knowledge and fosters a collective ethos focused on responsible and informed food sourcing.
Tips for Maintaining and Updating Your Log
Maintaining and updating your foraging log is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and relevance of the information it holds, which is key to effective foraging practices in urban settings.
By regularly revisiting and revising your log, you enhance your own knowledge and contribute to the community’s collective understanding. This practice fosters a vibrant culture of sharing and collaboration among fellow foragers, enriching everyone’s experience in the field.
Start documenting your foraging experiences now to connect with nature meaningfully and inspire others to do the same!
Organizational Strategies
Use effective strategies for your foraging log. This makes it easier and more accessible for everyone involved.
You and your fellow foragers can optimize food mapping and streamline data management.
Consider labeling, using digital tools, or adding visual aids to sort your findings based on location, season, and plant type. This approach helps you easily manage resources.
Utilizing apps designed for tracking your foraging activities can help you upload photos and notes. Color-coded systems or charts can visually highlight the abundance of certain species.
By embracing these innovative practices, you minimize food waste and contribute to the sustainability of the ecosystem. This fosters a community rooted in environmental awareness and responsible consumption.
Sharing Your Foraging Locations
Sharing your foraging spots builds community and improves the experience. But be cautious of the risks, like over-foraging and habitat disruption.
By understanding food ethics and community engagement, you can make well-informed decisions about how to share your expertise safely and responsibly.
Benefits and Risks of Sharing
Sharing locations offers huge benefits. You access more edible species and strengthen community ties.
However, it also carries risks like resource depletion and disputes over location ownership. By understanding these dynamics, you can make responsible choices that support both ecological conservation and community harmony.
In urban foraging communities, you can discover a wealth of nutritious, locally sourced food resources. This fosters a deep connection to nature, even in a bustling cityscape.
The spirit of collaboration encourages knowledge-sharing about effective techniques for utilizing foraged items and identifying invasive species that could threaten local ecosystems.
As more foragers flock to popular spots, the risk of depleting certain species increases. This sparks discussions about the ethics surrounding foraging rights and responsibilities.
Striking a balance between accessibility and sustainability is crucial as you navigate the complexities of harvesting food while ensuring the environmental health of your surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is considered a foraging location?
A foraging location is any place where food is gathered, like forests or fields.
Why is it important to document foraging locations?
Documenting foraging locations helps researchers and conservationists track food sources, and learning how to document your foraging journey aids in population management and conservation efforts.
How do I document a foraging location?
To document a foraging location, take notes on the plants and animals present, the season, weather conditions, and any other relevant information. You can also check out how to document my foraging finds for additional tips, or create a map of the area and take photos.
What should I include in my documentation of a foraging location?
Include the date and time of your observations, as well as factors impacting food availability, like human activity or climate change.
Can I document foraging locations for personal use?
Yes, you can document foraging locations for personal use, like foraging for wild edible plants. For more insights, consider learning how to record and share your foraging experiences. Just remember to check local regulations or restrictions on foraging in certain areas.
How can I contribute my records of foraging locations to scientific research?
Join the movement to document your foraging finds! Community science groups collect and analyze data on foraging locations.
You can also reach out to local universities or research institutions to see if they are doing research on foraging behavior in your area.